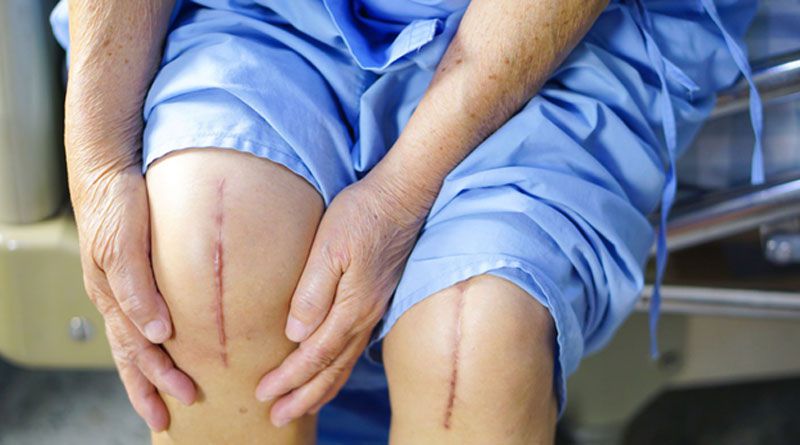
Introduction to knee replacement surgery
Dr. Sandeep Singh, the leading orthopedist in Bhubaneswar says, knee replacement surgery involves replacing a broken or worn knee joint with an artificial joint. ‘Arthroplasty’ is the medical word for this sort of surgery. Knee replacement surgery (arthroplasty) is performed to reduce pain and increase mobility in the knee. Depending on the condition of the knee, there are two types of knee surgery:
- Total knee replacement: If the entire knee joint is injured, this procedure may be required.
- Unicompartmental or unicondylar knee replacement: This is sometimes known as a partial (half) knee replacement. If only one component of the knee joint needs to be replaced, this is done.
When the articular cartilage in the knee joint is injured or worn away, it causes pain and difficulties moving the joint. This means that instead of moving over each other smoothly, the ends of the bones begin to rub or grind against each other. The use of an artificial knee joint to replace a damaged one can assist in relieving pain and improve mobility.
In India, osteoarthritis is the most common reason for knee replacement surgery. Osteoarthritis develops when the articular cartilage in the knee is injured or worn away due to normal wear and tear.
When should a knee replacement be performed?
If you’ve exhausted all non-surgical options and your discomfort persists even when you’re sleeping, you’ll require knee replacement surgery (arthroplasty). This is because any surgery includes some risk; knee joint replacement surgery is usually suggested only after all other non-surgical options have failed.
There are several non-surgical options for treating knee discomfort, including:
- Weight loss,
- Physiotherapy to strengthen the muscles around the knee and relieve joint tension
- Using a cane or crutch as a walking aid, or
- Anti-inflammatory drugs, pain relievers, and steroid injections to reduce inflammation and pain.
The majority of persons who have knee replacement surgery in India are between 60 and 80. For younger patients, all nonsurgical options are more likely to be recommended. Knee replacements are also more likely to endure longer in persons who are older and less active.
However, as the technology utilized in India’s most extraordinary knee replacements has evolved, younger or more active people are now seeing better results from knee replacement surgery. Anyone having knee replacement surgery, regardless of age, must be physically fit and healthy enough to handle a significant operation and the recovery and rehabilitation that follows.
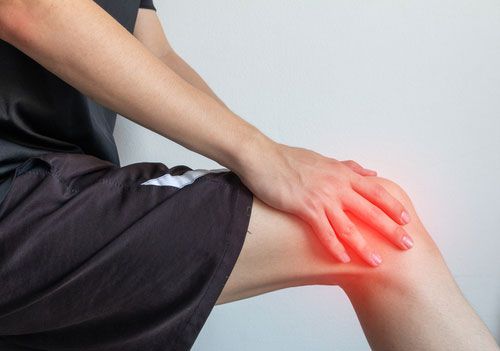
Knee replacement complications
All operations, according to one of Bhubaneswar’s best orthopedists in, have a little risk. The majority of people, on the other hand, do not experience any difficulties. Knee replacement surgery (arthroplasty) is currently a popular and standard procedure in India. Total knee replacement is intended to alleviate pain, improve quality of life, and improve knee function.
Evidence suggests that if the surgeon is knowledgeable with the treatment and uses advanced technology such as the NAV3 computer navigation technique or a robot, the risk of problems is minimized, and patient satisfaction with the outcome is raised.
Infection: You run the chance of getting an infection following your surgery. Because of tight OT protocols and pre-operative patient optimization, the incidence has been exceedingly low (less than.01 percent). Following your knee replacement, you may need to take antibiotics to avoid dental work or other surgeries. This is to prevent an infection from spreading to your new knee from elsewhere in your body.
Excessive bleeding: If you experience excessive bleeding after surgery, you may need a blood transfusion to replace the blood you’ve lost. Since I began using NAV3 electronic navigation, this has become increasingly rare.
Scarring: Where the incision was made on the front of your knee, you will have a scar. You may also experience numbness around the spot in rare circumstances. This numbness may not go away entirely in some instances.
Blood clots (thromboses) can form in the deep leg veins (deep vein thrombosis) due to limited leg movement in the weeks following surgery. They can be avoided by wearing special support stockings, walking or exercising immediately after surgery, and taking anticoagulant medications.
Knee Replacement Recoveries
Dr. Sandeep Singh, Bhubaneswar-based best orthopedist, says you’ll probably need to stay in the hospital for 4 to 6 days, depending on how well you recover and what type of knee replacement you’ve had. Patients who have had a half-knee replacement surgery usually stay in the hospital for a shorter period. You will see a physiotherapist during your hospital stay who will show you some exercises to help you recover quickly.
You will be able to move around with the help of a frame, walker, or crutches for a few days. After about a week, these will be replaced with walking sticks. You’ll likely be told to keep using the walking stick until you’ve been re-evaluated at your hospital follow-up appointment. This appointment is usually six weeks following your surgery.
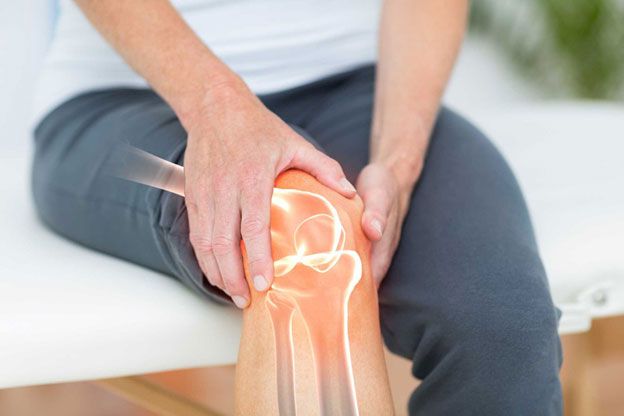
Your surgical wound (arthroplasty) will be covered until it has healed completely. 2–3 weeks after surgery, any staples or stitches in your injury will be removed. In the hospital, your physiotherapist will give you an activity schedule. Because these exercises are so crucial to your rehabilitation, you must keep doing them once you get home.
Short walks and routine home tasks, such as walking up and downstairs, are recommended. These exercises can help you regain your mobility while also strengthening your muscles. 3-6 weeks after surgery, most patients can resume typical leisure activities. Your swelling, on the other hand, could take up to three months to subside.
You can resume driving as soon as you can bend your knee enough to get in and out of a car and maintain reasonable control. This usually is four to six weeks after surgery, but you should consult with your physiotherapist or doctor to ensure that you are safe to drive. The majority of individuals can return to work around this time; however, it depends on how physically demanding your job is.
To get the most out of your knee replacement, you’ll need to keep doing the exercises and following the rehabilitation guidelines given to you. Surgery alone will not ensure greater mobility or pain relief.
What is the expected lifespan of the replacement knee?
Your replacement knee will not endure indefinitely because of normal wear and tear from everyday use. Your new knee will most likely survive at least 20 to 25 years. This can be done and possibly increased by taking adequate care of your new knee and avoiding overstretching it. You may be recommended to prevent some activities, such as running or high-intensity aerobics.

Namaste UI collaborates closely with clients to develop tailored guest posting strategies that align with their unique goals and target audiences. Their commitment to delivering high-quality, niche-specific content ensures that each guest post not only meets but exceeds the expectations of both clients and the hosting platforms. Connect with us on social media for the latest updates on guest posting trends, outreach strategies, and digital marketing tips. For any types of guest posting services, contact us on info[at]namasteui.com.