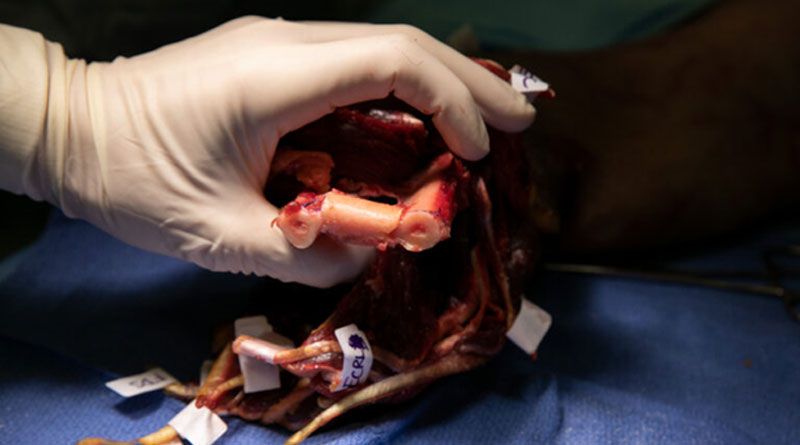
In reimplantation surgery, any cut component of the body is reimplanted, which requires reattaching it to its original position. This is a cutting-edge microsurgical method that is rapidly being used around the world. Many of these cases are conducted on a regular basis in India at a few select institutes.
In This article, Dr. Leena Jain who is one of the best plastic surgeons in Mumbai will discuss everything you need to know about reimplantation surgery.
What should you do if a portion gets cut?
Wrap the part in a moist towel or gauze, place it in a plastic bag, and then place the bag in an ice box. The part should never be placed directly on ice or in water or any other liquid. Wherever feasible, apply pressure to the severed stump with a clean cloth or pressure dressing. Patients should be taken to the nearest tertiary care center for microsurgery as soon as possible.
When you get to the hospital, what happens next?
The portion is then washed and examined under a microscope in the operating room. It’s all set to be reinstalled. Meanwhile, the patient is being investigated by the plastic surgeon, with basic blood tests performed and sufficient blood arranged as needed. Blood is required depending on the part of the body that has been severed. The patient is then taken to the operating room. The severed stump is sewn back together with all of the cut structures. Metal wires are used to secure the bone (in cases of upper or lower limb replantation). Tendons that are essential for moving the component are repaired next (if applicable). The arteries, veins, and nerves are then repaired micro-surgically. A proper dressing is applied, as well as a splint if necessary.
What are your chances of being successful?
The likelihood of success is determined by a number of factors, including:
The following are some of the most common steps in the process:
Cut type: A sharp cut has a considerably better probability of healing than a crush or avulsion damage. Avulsion is a process in which a portion is abruptly yanked or twisted out, as in a washing machine damage.
Smoking: Patients who smoke on a regular basis have a larger likelihood of failing than those who do not.
Multiple level injury: Usually bad outcomes, therefore reimplantation is not attempted.
Other diseases: Diabetes and vascular disorders are examples of comorbidities that have lower results.
What can you expect just after surgery?
IV fluids and blood-thinning medicines will be administered. There could be pain at the surgery site, prompting a higher dose of pain reliever.
In every case of reimplantation, the restored blood arteries are at danger of becoming blocked at any moment following surgery, most typically in the first – third days. The surgeons and specialized personnel will keep a close eye on the patient, and if a problem is discovered, the patient may need to be sent to the OT for treatment.
A patient is usually discharged on the 5th – 7th day after surgery. Prior to discharge, the dressing may or may not be changed.
Following Replantation, Recovery

Physiotherapy is started after one month following hand replantation under professional supervision at the hospital. The splint will be worn for two months, after which strengthening exercises will begin and normal activities will resume after three months. Depending on the region of replantation, it takes around a year for sensation to return. Functional outcomes are poorer for reimplants with fused joints than for those with intact joints.
The extent of recovery is determined by factors such as:
Patient age – patients who are younger have better results than those who are older.
Smoking – Nonsmokers had a superior functional result and survival rate than smokers.
Physiotherapy – Regular physiotherapy is required in cases of hand and foot reimplantation in order to get a positive outcome. If a patient does not follow the instructions for physiotherapy, the reimplanted hand or finger may become stiff and non-functional.
Diabetes – diabetic people heal more slowly and are more susceptible to infection.
Follow-up Surgery – A large number of people require subsequent surgery to improve their function.
What can you expect from replanting amputated limbs?
It is impossible for the patient to restore 100 percent of his or her pre-injury functional level. A recovery of 60-70 percent function after reimplantation of the hand is regarded a remarkable result; but, in cases of isolated fingers, the functional outcome can be even better. It depends on the area of the body that was amputated, the type of amputation, the patient’s age, nutritional health, and how closely he or she follows the exercise routine.

Namaste UI collaborates closely with clients to develop tailored guest posting strategies that align with their unique goals and target audiences. Their commitment to delivering high-quality, niche-specific content ensures that each guest post not only meets but exceeds the expectations of both clients and the hosting platforms. Connect with us on social media for the latest updates on guest posting trends, outreach strategies, and digital marketing tips. For any types of guest posting services, contact us on info[at]namasteui.com.